The article was updated on 27.06.2024
Nowadays, having an IBAN number is common, especially within European financial institutions. Still, some might wonder why IBAN codes are so long or why they were created if SWIFT codes were already a thing.
This Genome article will cover the above questions, as well as explain how to send money using an IBAN number and the overall significance of IBAN numbers in online banking.
What is an International Bank Account Number (IBAN)?
IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number. The European Committee for Banking Standards established the International Bank Account Numbers in 1997 to make money transfers safer and more convenient.
IBAN numbers can consist of 34 characters maximum, and the length varies from country to country. Some countries have only 15 characters in their IBANs, while others have more than 20. Yes, dealing with a lengthy IBAN format does not seem easy initially, but let’s dive into what it stands for.
Here’s a standard IBAN example – EE38 2200 2210 2014 XXXX.
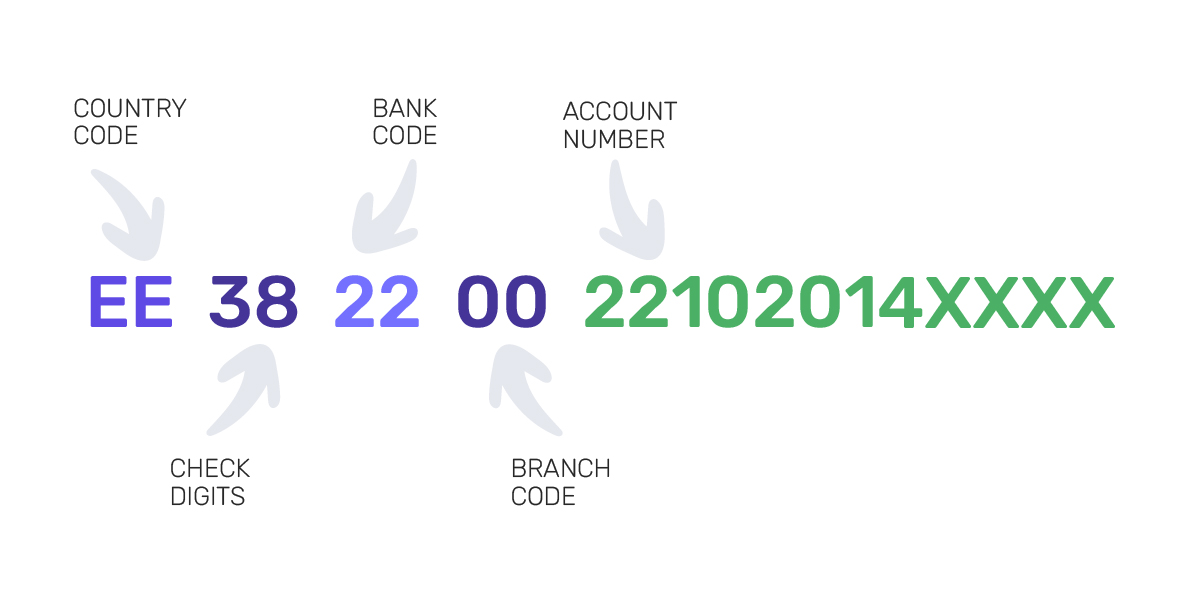
1. An IBAN starts with two letters that show the two-letter country code (ISO/location code of the country). For example, GB stands for Great Britain, HU – for Hungary, EE – for Estonia, etc. An IBAN number will always start with the country code letters.
2. The two digits next to an ISO code are check digits – an essential part of an IBAN number that allows detecting if there are any errors. This code is calculated through the MOD97 algorithm, in which the rest of the IBAN digits are used. Thus, if you refer to an incorrect number, the checking figures will help to spot that during the validation process.
The next part of an IBAN number is a Basic Bank Account Number (BBAN), a bank account number specific to every country. It consists of a bank code, a branch code, and the number itself.
3. A bank code is a set of digits representing a banking institution where you opened an IBAN. The length of a bank code differs and can contain both numbers and letters. For instance, the bank code “2100” stands for Spanish CaixaBank, and “BKEN” is a Bank of England. A lengthy “3704 0044” code is for the German Commerzbank. The code “22” used in our example stands for Swedbank.
4. Next is a branch code, by which you can identify the banking branch which holds the account. Not all IBANs contain this code. Here, the branch code is “00”.
5. The rest of your IBAN is the number of the account, which can also contain letters. In our case, it’s 2210 2014 XXXX.
Please note that in some cases, the IBAN code ends with a second set of check digits, for instance, for French account users. You also can check what your IBAN consists of online on Bank.Codes and similar sites.
Purpose of an IBAN number
The IBAN system is used as a more precise method of detecting whether the transaction details are correct, minimizing the number of errors that can occur during international transfers.
The IBAN identifies crucial information such as a country, bank, and bank account number. All these are gathered together when instructing and receiving domestic/international transactions. This way, the payer can transfer money to the exact account number they intend to.
Even though the IBAN system seems to be a complex code, it brings clarity and order into the vast network of international payments and bank accounts. By providing the correct IBAN, you can be sure your money will be settled into the correct account.
The IBAN registry is the catalog of all countries that use IBANs. It contains general information regarding IBAN numbers. For instance, the registry contains the length of both BBAN and IBAN, whether the country belongs to the SEPA zone, and even the contact details of the national bank.
How is an IBAN used?
An IBAN is used for international and domestic transfers to identify the beneficiary’s bank account and other necessary details. The information the IBAN contains allows errors to be avoided when sending an international transaction.
How to use an IBAN for sending and receiving payments
IBAN is necessary for cross-border payments within Europe and to other countries. It is especially common for SEPA payments. If you own a bank account in euros, you also have an IBAN number.
To send money to another IBAN, you need to know the person’s IBAN and BIC and fill in these numbers when transferring funds. You may also be required to enter the beneficiary’s name and address, as well as the payment description.
Here’s how the IBAN number is used during a transferring process inside Genome:
For instance, you want to make a SEPA credit transfer. To do so:
Open the app or the web version of Genome;
Go to the Transfers menu and select the Bank transfer option;
To send a payment via SEPA, select an account in euros;
Fill out the beneficiary’s name, IBAN, and SWIFT code (bank identifier code).
Fill out the payment description and send the payment.
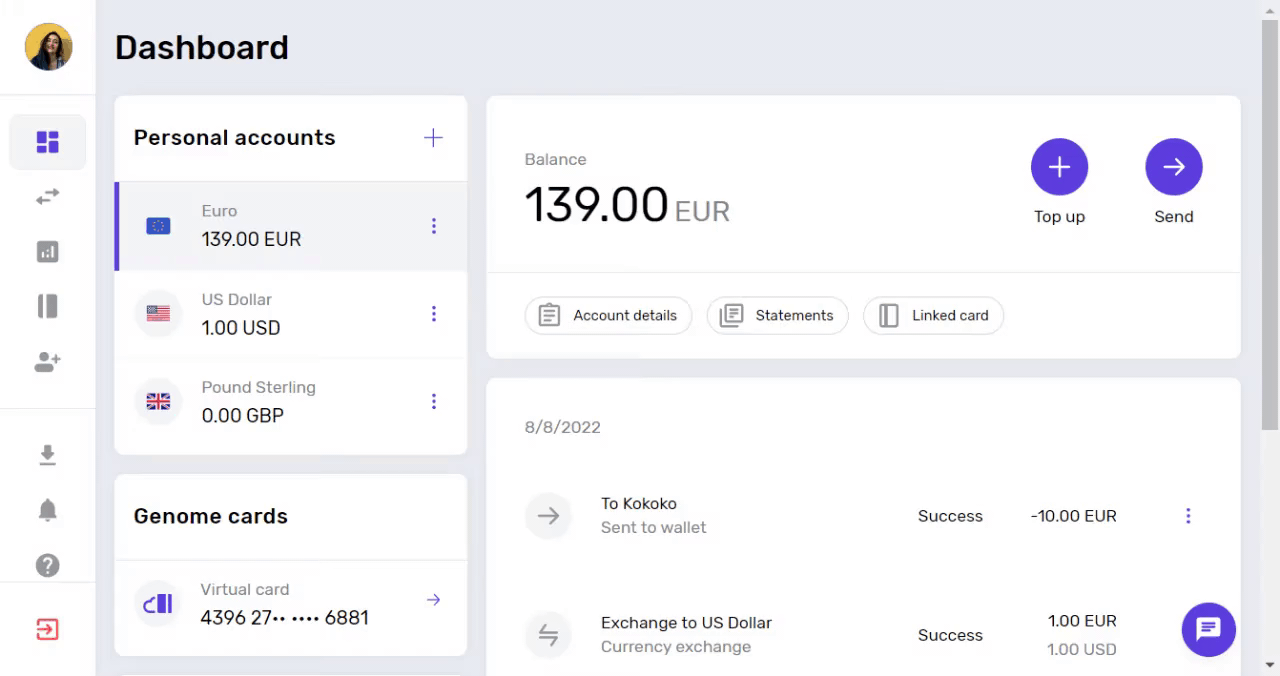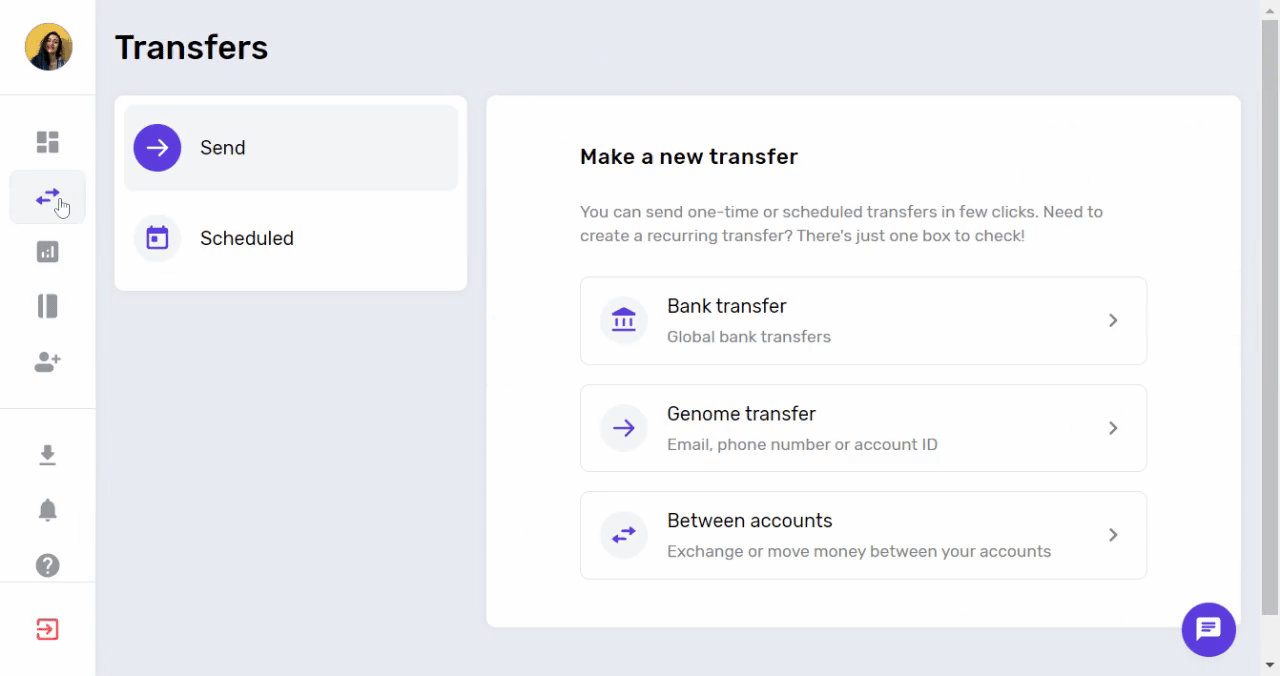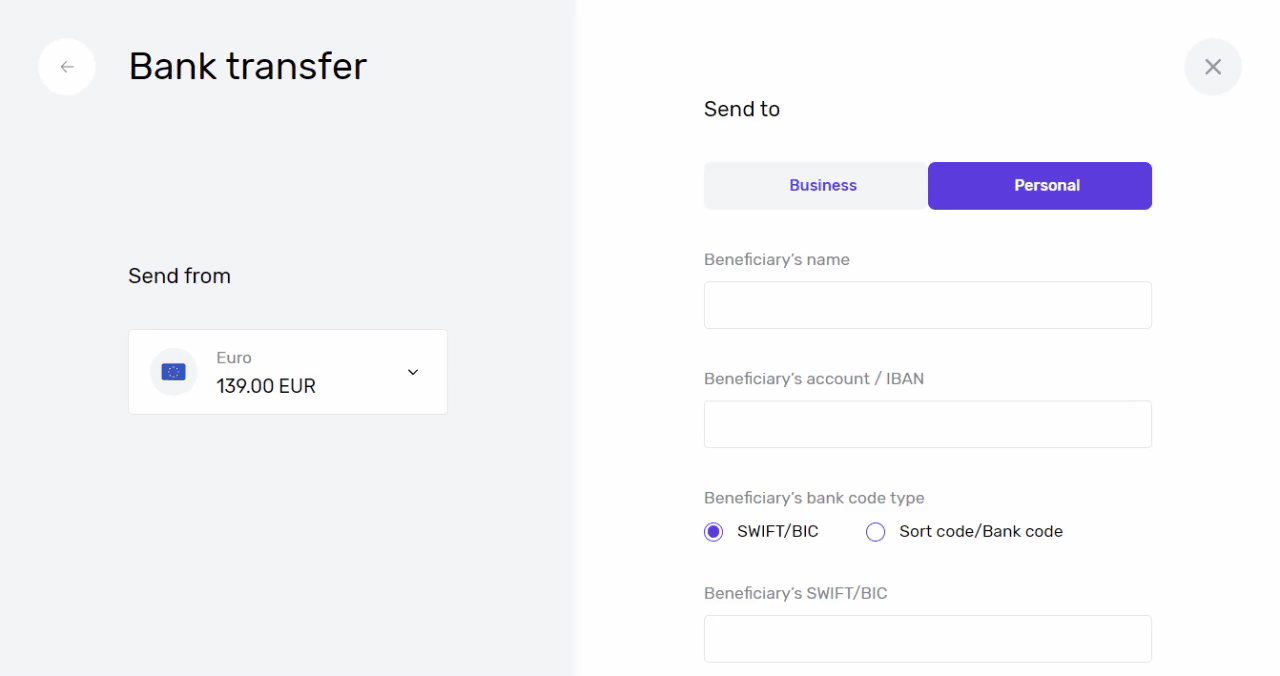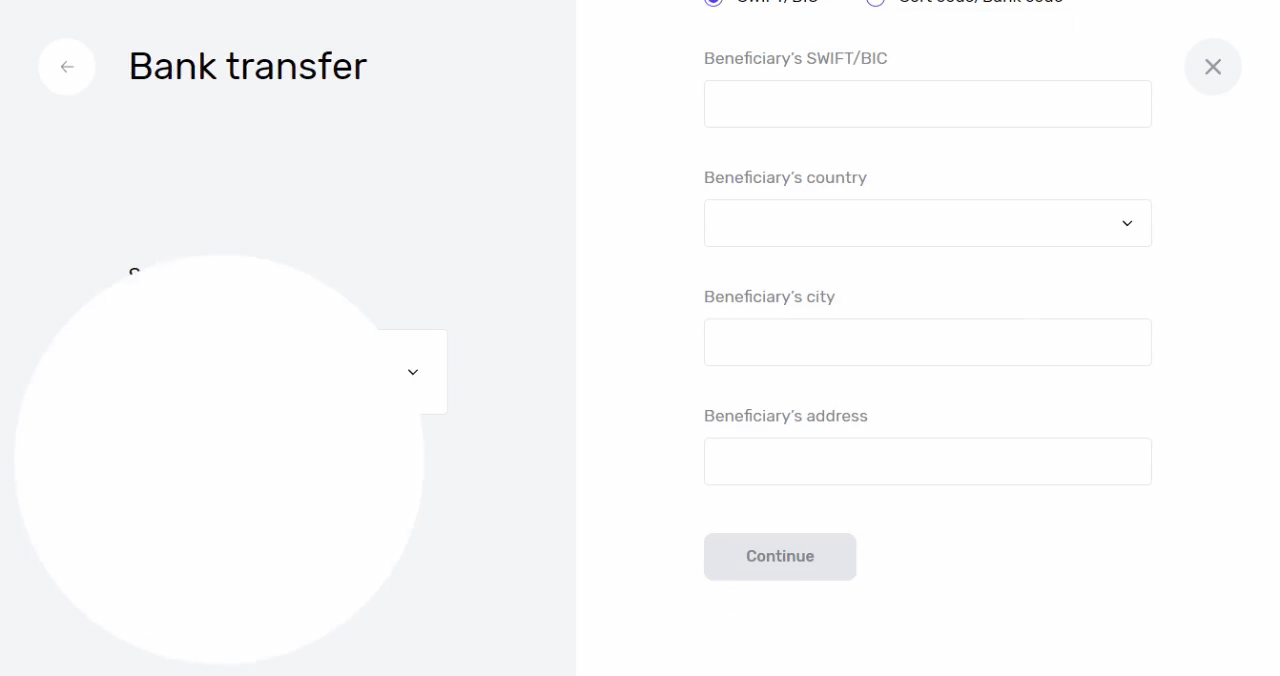
If you want to receive a SEPA transfer with the help of an IBAN, select one of your euro accounts on the dashboard and open account details. Copy the details and send them to the payer.
Importance of IBAN numbers
Establishing IBANs was important for making the transfer process more secure and fast, as extensive information inside the IBAN makes it easier to identify the beneficiaries.
Moreover, the standardization of IBANs ensures compliance with electronic money regulations and major financial system rules.
How to find your IBAN number
You can find your IBAN number by doing the following:
IBAN numbers are always mentioned in an official bank statement;
You can look up the IBAN code in your banking app;
You can always contact your financial provider via customer support or go directly to the bank’s branch to receive this information.
If you use Genome, you can find your IBAN code and other account details in just three clicks:
Go to my.genome.eu or open the app and log in;
When on your dashboard, select any account you have in euros;
Open the “Account details” tab and find your IBAN number there.
Common misconceptions about IBAN
Although IBANs are very common, there are still some mix-ups about them and how they work in the online banking sphere.
IBAN is not a new account number
IBANs are not new bank account numbers. In fact, your individual account number is included in the IBAN, along with the two-character country code and a bank code.
Not all countries use IBANs
Though IBANs were originally meant to be used within the European Union, they were successfully embraced by other countries.
Right now, there are 77 countries and territories listed in the IBAN registry, including all 27 members of the EU. Notably, the US and Canada don’t use IBANs.
IBANs and SWIFT codes (bank identifier codes) differ
Both the SWIFT system and IBANs are integral for sending money abroad and domestically.
SWIFT stands for the Society for Worldwide Interbank Financial Telecommunication and is internationally recognized. The SWIFT network was established in 1973 to transfer information for performing international transactions and uses SWIFT codes for this purpose.
A SWIFT code (BIC) is a set of 8 to 11 characters used for the identification of a specific bank or its branch in cross-border transactions. The SWIFT code includes a bank code and the location code of the financial institution. The last 3 digits in a SWIFT code identify the branch. Sometimes, the branch isn’t specified, and the SWIFT code will only have 8 characters.
To avoid errors, IBAN contains a lot more information about individual bank accounts, while SWIFT covers the identification of the specific financial institution. However, you usually still need both to make an international payment to another IBAN. SWIFT codes and IBANs work in pairs to ensure a smooth, speedy, and secure experience when sending money abroad.
Ensuring secure transactions with IBAN
All in all, Using IBANs, domestic and overseas banks identify beneficiaries more accurately. It allows for preventing mistakes and inaccuracies.
To ensure you have no issues, always verify the IBAN with the beneficiary or through an official IBAN validation before making a payment.
If you need an IBAN to transfer funds, look no further than Genome! Our personal and business wallet users get access to secure dedicated IBAN accounts, allowing them to send and receive SEPA transfers with ease!
You can instruct payments in just a few minutes – send them immediately or schedule them for later. Business wallets also access batch payments, allowing them to send up to 3000 transfers at once!
Moreover, Genome’s multi-currency account feature enables you to have up to 5 accounts in euros, as well as other currencies – USD and GBP.
The role of IBAN in modern banking
Of course, not all banks use IBANs to facilitate the transfer process, as the IBAN was primarily introduced for payments within the EU. However, since the launch of this technology, more and more international banks outside the EU have implemented IBANs. More than 70 countries are in the registry, including some of the Middle East and Asia territories.
One of the primary reasons is that IBANs really help standardize international transactions, enabling the system of safer and more accurate transfers.
As time passes, it’s safe to assume that even more countries will appear on the registry thanks to the convenience and reliability of IBANs.
Conclusion
IBANs are crucial for ensuring accurate and safe transfers, especially if you send and receive payments within Europe. Consider getting an IBAN if you live or work in the EU.
Genome can help! You can have multiple IBANs, open personal and business accounts, exchange currencies, and transfer money abroad. The onboarding is easy and takes place completely online. Feel free to contact our support team at support@genome.eu.
FAQ
What is an IBAN number, and why is it important?
IBAN stands for International Bank Account Number. These are used for a more accurate domestic and international transfer process, as they contain information about the beneficiary’s bank and are used for identifying bank accounts.
How do I find my IBAN number?
You can use your mobile banking service — your IBAN should be available in the Account details section in your financial provider’s mobile or web application. Bank statements with all your account information are probably the most common way to share the information needed for making a transaction. Finally, you can contact your financial provider to obtain information about your IBAN.
Can I use an IBAN for domestic transactions?
Yes, you can use an IBAN for domestic transactions if your country supports IBANs.
What happens if I use the wrong IBAN for international payments?
Financial institutions usually check the payment details before sending the payment, so if you make a mistake, your transfer won’t be sent.
How do IBAN and SWIFT/BIC codes differ?
IBAN and BIC/SWIFT codes are two different numbers that hold essential information for making international money transfers. IBANs provide data on one’s bank account, while BIC codes (bank/business identifier codes) determine the correct bank and branch codes.






